Over the past few years, demand for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies has been growing exponentially. Meeting this demand is no easy task, but recent innovations have made it easier for just about anyone to trade it.
Cryptocurrency ATMs—like their name suggests—allow you to do just that.
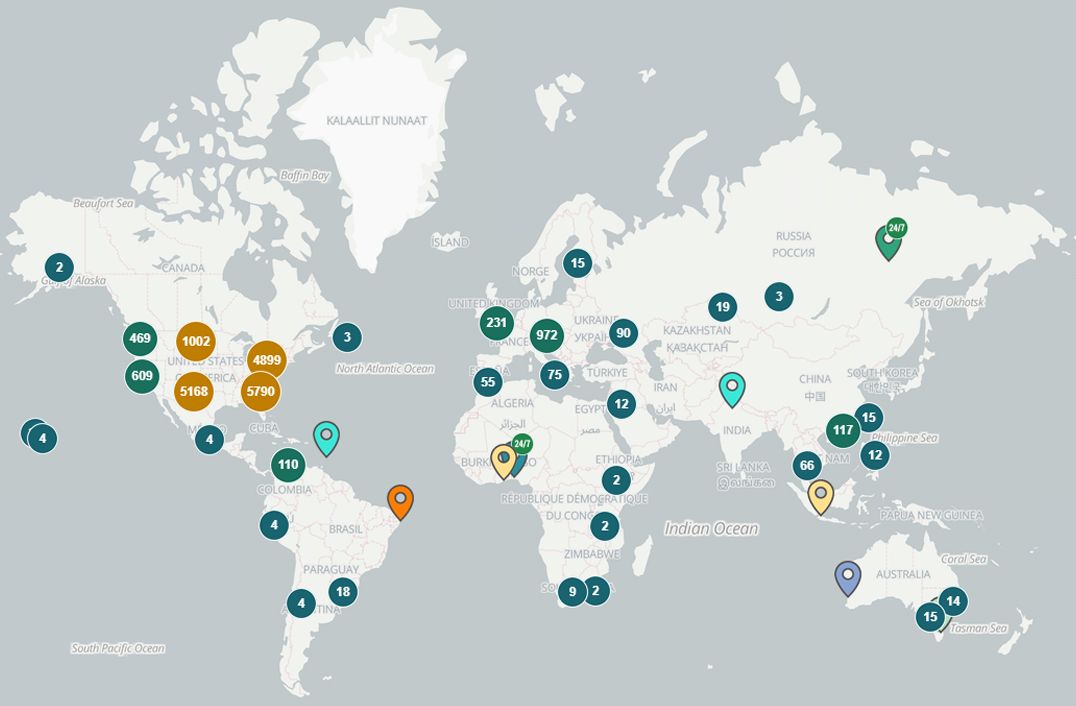
There are over 19,000 cryptocurrency ATMs spread across the world. You can use one to buy and sell digital currencies at a physical kiosk—drastically reducing the difficulty of owning and acquiring these assets.
How Does a Bitcoin ATM Work?
Even though they share a name, Bitcoin ATMs are nowhere near the same as traditional, bank-operated ATMs that have been around us for decades. First and foremost, the funds you deposit or withdraw at cryptocurrency ATMs don’t go through a bank account. Instead, they simply allow you to exchange digital currencies such as Bitcoin for cash or vice versa.
The process is simple: Approach a crypto ATM and read the instructions on-screen. If you’re looking to buy crypto, the machine will ask you to input the amount. Then, open your cryptocurrency wallet and generate a new receiving address and QR code. Once scanned, the machine will prompt you to deposit cash to finalize the trade.
The process of selling Bitcoin to a cryptocurrency ATM is fairly similar. You’ll simply be asked to send funds to the ATM instead of the other way around. Once the transaction is successfully reflected on the ATM’s end, an equivalent amount of cash will be dispensed automatically.
Why You May Want To Use a Crypto ATM
Bitcoin ATMs first became popular as a means to quickly and easily acquire cryptocurrency. Several years ago, they were an extremely popular option when large trustworthy cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase, Gemini, and Kraken simply did not exist.
Today, they still have their place since they are the only way for you to trade physical cash for cryptocurrency directly.
Bitcoin ATMs do not rely on slow bank transfers or verification processes that are prevalent at many exchanges. Consequently, they are often used by individuals looking to keep a clean digital trail and maintain the security of their identities.
That being said, it’s worth noting that many countries have regulations that require Bitcoin ATMs to identify users. In that case, you will be required to verify your phone number before initiating a transaction.
Furthermore, most ATMs have considerably lower transaction limits due to the lack of full-fledged identification procedures. Unless you complete a KYC process with the ATM operator, governments will not be able to track your tax liability. To prevent this loophole from being exploited, Bitcoin ATMs may only allow you to buy or sell small amounts of cryptocurrency.
How Do You Find a Nearby Bitcoin ATM?
Coin ATM Radar offers a free web and mobile app that tracks the availability of cryptocurrency ATMs around the world.
Since cryptocurrencies are decentralized, just about any business can decide to install an ATM on their property. Many business owners do this to increase foot traffic through their property or improve their brand image. This is why you are most likely to find a Bitcoin ATM at shopping malls, convenience stores, and coffee shops—locations that you would want to visit pretty frequently.
Security is usually not a concern since the machines are programmed directly by the operator of the ATM. In other words, all ATMs will behave exactly like each other, provided they’re backed by the same manufacturer.
When You Should Not Use a Cryptocurrency ATM
A cryptocurrency ATM prioritizes convenience above everything else. Unfortunately, this comes at quite a hefty price. Bitcoin ATMs, in particular, will typically charge you anywhere between 7-20 percent of your total amount as a transaction fee. Fees lower than that are almost unheard of in the cryptocurrency ATM space, while there is no real upper limit.
While a portion of this fee goes directly to the ATM owner and operator, a significant amount is likely used to offset Bitcoin’s own network fees. Unlike online cryptocurrency exchanges, which provide you with a wallet, these ATMs need to initiate an on-chain transfer every time you transact with them. However, when the network is busy, fees can skyrocket as everyone competes for the fastest transaction settlement times.
Fees and Other Charges
The same variability of network fees does not deter exchanges because they retain custody of all user funds—even if the cryptocurrency was traded between two users on the platform. Network transfer fees only come into play when you ‘withdraw’ your balance from the exchange to a wallet of your choice.
Furthermore, even if ATMs do not charge an egregious transaction fee, a small proportion of them offer a worse buy/sell price compared to the prevailing exchange rate. For example, an ATM may sell you Bitcoin at the rate of $55,000 instead of the $50,000 it would cost you on an exchange. In more practical terms, a $100 transaction will net you only 0.001818 BTC instead of 0.002 BTC.
This 10 percent difference is not omnipresent—many ATMs follow global rates much more accurately. Even then, they may only update their prices every few minutes. Given the volatility of the cryptocurrency market, you may not be able to take advantage of sudden dips in the exchange rate. This is the same concept as paying a higher rate at a foreign currency counter in an airport.
Bitcoin ATMs Are Good for Privacy but Very Expensive
The best way to ensure you’re getting a fair exchange rate is to visit a cryptocurrency exchange rate tracking website such as CoinMarketCap before locking in your purchase on the ATM.
You should especially consider avoiding Bitcoin ATMs that charge you a transaction fee and impose a large premium on the exchange rate. For larger and more frequent transactions, you may also be better off using a cryptocurrency exchange. This is because they often charge lower fees and offer convenient year-end reports for you to analyze your tax liability.
Image Credit: Elise/Pexels, Bitcoin ATM Map/Coin ATM Radar