The Terminal app is the gateway for command-line access in macOS. If you frequently find yourself working inside Terminal and want to play an audio file, there's no need to leave the app. There are commands that you can use to not only play audio files directly from inside Terminal, but to convert audio files as well.
How to Play an Audio File in Terminal
First, launch the Terminal app on your Mac from Applications > Utilities or from Spotlight. To play an audio file from inside Terminal, run the afplay command followed by the path of the audio file you want to play.
For example:
afplay /Users/itechno8/Downloads/file.wav(To get the file path for any file, simply select the file in Finder and press Cmd + Option + C to copy it to your keyboard.)
Once a song starts, you can stop the afplay command by pressing Control + C.
You can also choose to close the Terminal window after starting a song; this will keep the song playing in the background, but you need to change the command you use. To do this, add & disown after the path to the audio file:
afplay /Users/itechno8/Downloads/file.wav & disownOnce you close the window, you might get a warning that closing Terminal will terminate the afplay process. Select Terminate and the window will close. You'll find that the song will keep playing nevertheless.
If you want to stop the audio playing after you've closed the window, you'll need to open up Terminal again and run a killall command to stop it:
killall afplayHow to Get Information About an Audio File in Terminal
You can use the afinfo command in Terminal to get specific information about an audio file. Simply type the command followed by the path of the audio file. For example:
afinfo /Users/itechno8/Downloads/file.wav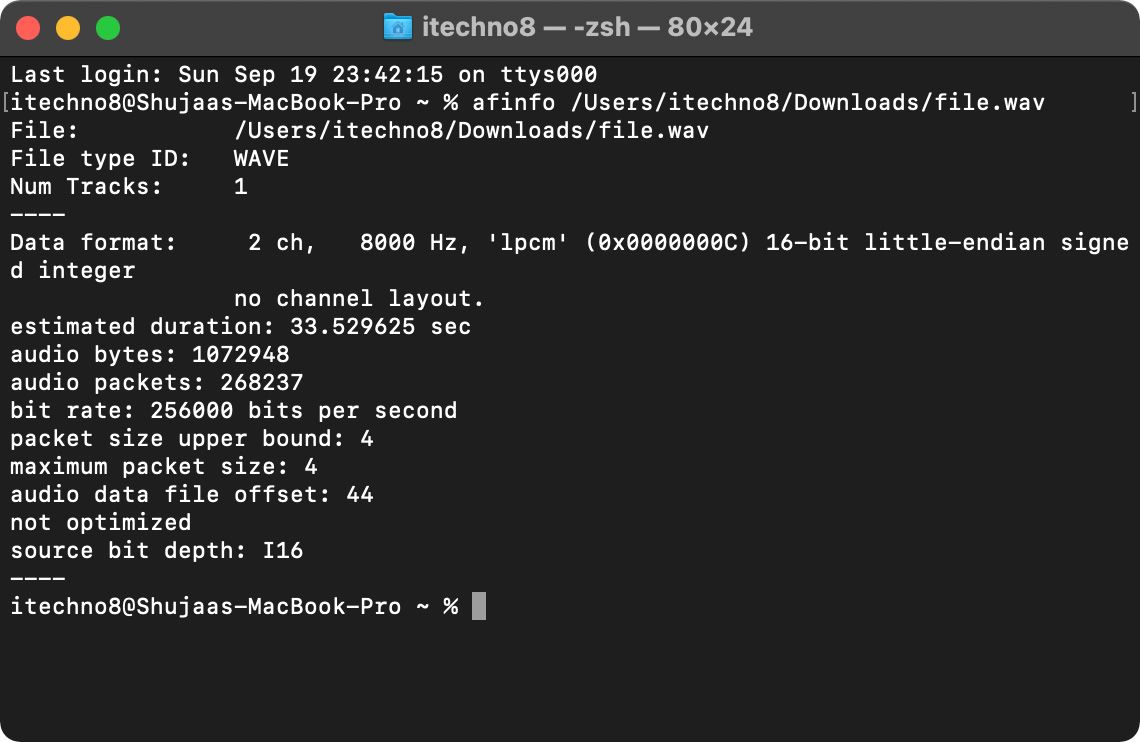
How to Convert Audio Files in Terminal
Audio files can also be converted from one format to another from within Terminal. The afconvert command allows you to do this. They are many complicated uses of this command, but we'll be focusing on simply converting one audio file format to another.
To do this the easy way, open up the folder which contains the file you want to convert. Control-click on the main folder and select New Terminal at Folder.
The general format for the afconvert command is as follows:
afconvert -f FORMAT -d CODEC SOURCEFILE [-o DESTINATIONFILE]It is necessary to specify both the file format and the codec. Otherwise, an error will appear. If you omit the -o option, afconvert will automatically pick a name and extension based on the other inputs.
An example of this command in use is as follows:
afconvert -f M4AF -d LEI32 Original.wav [-o Converted.mp4]This converted my WAV file "Original.wav" into an MP4 file "Converted.mp4".
It's important to note that macOS does not ship with an MP3 encoder by default, and hence you might face some difficulties while converting mp3 files from the Terminal window without a third-party encoder. To get a list of the supported formats, use the following command:
afconvert -hfFor more help with the afconvert command, try running this:
afconvert -hPossible Uses for the Commands
There are many uses for the commands explained above. You can use the afconvert command to automate the process of converting multiple files or you can use SSH to access your Mac from another Mac and use Terminal play some audio through the speakers. To astonish a coworker, perhaps?
![How to Find IMSI Number on iPhone [Helps with iOS Unlock][Updated] data:post.title](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjLjHwhnfUXNJTuiylqmlurhLRVAEVi803j6xcnvN8EZwF5_XUynz1y0Ko-vwpx6O3nT5hogTELahedGzgQpXM5Y99fcBliinyBu8ACw8_DVV3FpPLkIqR0u7v_HM39rAkpV5MyJiG1h5s/s72-c/find+imsi+iphone.jpg)