Did you know that Chromebooks have a built-in terminal? This terminal, known as the Chrome OS Developer Shell—or Crosh for short—lets you access a command-line interface that you can use to debug your machine, run tests, or just poke around for fun.
So, let's look at and test several terminal commands that all Chromebook users should know about for improved productivity and troubleshooting.
Essential Crosh Terminal Commands for Chromebooks
We'll explain all these in more detail, but here's the TL;DR version:
- Open Crosh: Ctrl + Alt + T
- Ping: ping [domain]
- Test memory: memory_test
- Configure modem: modem help
- Rollback Chrome OS: rollback
- Stop a process in Crosh: Ctrl + C
- Open Task Manager: top
- Battery Manager: battery_test [seconds]
- Developer Mode commands: shell, systrace, packet_capture
- Users and uptime: uptime
- Time settings: set_time
- Network diagnostics: network_diag
- Network trace: tracepath
- Help: help, help_advanced
- Memory information: free, meminfo
- Switch to the canary channel: live_in_a_coal_mine
- Auto-updates over cellular networks: update_over_cellular [enable|disable]
- Exit Crosh: exit
1. Open Crosh
You won't find Crosh in the regular list of apps in your Chromebook's app drawer.
To open Crosh, you need to press Ctrl + Alt + T, which will launch the terminal window in a new browser tab.
Note: You don't need to have your Chromebook's Developer Mode enabled to access Crosh.
2. Run a Ping Test
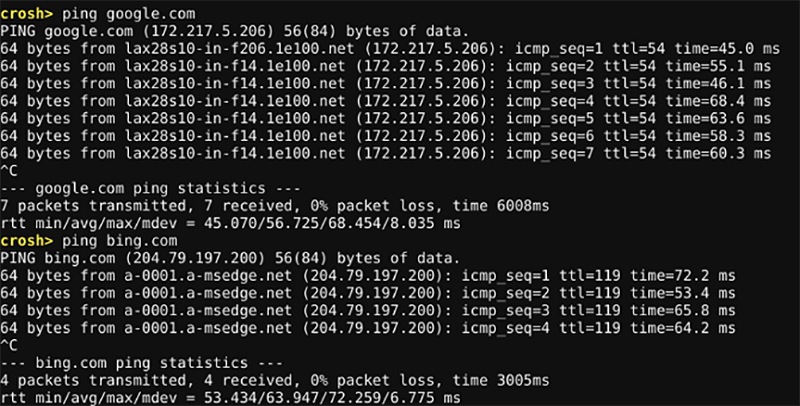
Type ping [domain] to run a ping test on your Chromebook. To check your network connection using ping, issue the following command:
ping google.comIn case you don't know, ping tests are an essential tool if you're trying to diagnose network issues. It will let you know how quickly traffic is traveling between your computer and a web server. It will also inform you if there are any dropped packets.
3. Test Your Chromebook's Memory
Although you can see information about your Chromebook's memory using third-party plugins (read our article about how to check your Chromebook's specs to learn more), it might not be enough for some users. If you want a more detailed level of information, use Crosh. Just type the following and hit Enter:
memory_test4. Configure Your Modem
A critical part of troubleshooting your network is ensuring that your modem is configured correctly.
Type the command mentioned below in the Chromebook's terminal. You will get access to a range of options, including settings to activate your modem, connect your modem, change the modem's firmware, factory reset your modem, and more.
modem help5. Reinstall an Earlier Version of Chrome OS
If a recent Chrome OS update has caused havoc with your computer, you can easily undo the changes and return to a previous version of the operating system using Crosh.
All you need to do is type the following command in Crosh and hit Enter:
rollback
6. Stop Any Process in Crosh
Suppose you want to halt any background process such as a ping or a memory test in Crosh. You can do so by pressing Ctrl + C. This method is better and safer than closing the Crosh window altogether.
7. A Better Task Manager
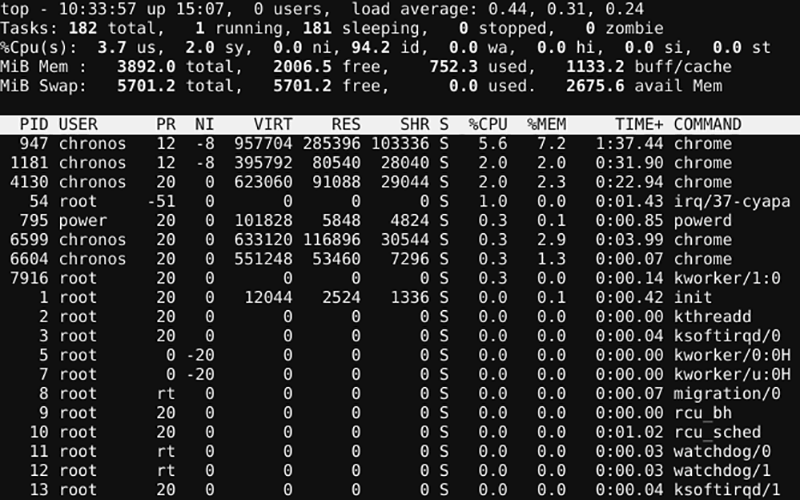
Very few people know that Chrome OS (and the Chrome browser on other operating systems) has its own task manager. It shows you what processes are eating through your CPU and memory. You can find it by opening Chrome and going to More (three vertical dots) > More Tools > Task Manager.
However, even fewer people know that Chrome OS has a secondary task manager hidden in Crosh. You can use it to learn about low-level processes that don't show up in the main task manager app. You can access it by simply typing:
top8. Battery Management
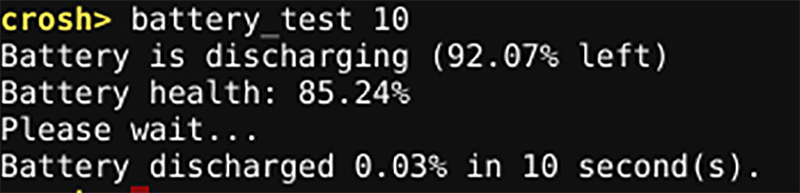
Again, you can see headline battery data merely by looking at the bottom right-hand corner of your Chromebook's screen.
However, if you want more information, type battery_test [seconds] into Crosh (replace [seconds] with a number). You can test this command by typing the following in the terminal:
battery_test 10Crosh will show you precisely how much battery power your machine used in the given timeframe, as well as feedback on your remaining battery time and your battery's overall health.
9. Developer Mode Commands
You don't need to be a developer to use Crosh. But, if you do have Developer Mode turned on, you will have three new commands available to you:
- shell: Opens a full bash shell
- systrace: Starts a system trace
- packet_capture: Captures and logs data packets
10. Users and Uptime
When was the last time you turned off your Chromebook? It might be days or even weeks between reboots.
You can use the below-mentioned command to see how long your computer has been running since its last shutdown. The results will also provide information about the users who are currently logged in.
uptime11. Change the Time
Do you have problems with your machine's display time? Perhaps you live on a border between time zones or have an internet connection with an IP address that frequently moves.
Enter set_time into Crosh, and you can override the operating system's time settings. For example, run the following command to change the time:
set_time 10 February 2021 11:21am12. More Network Diagnostics
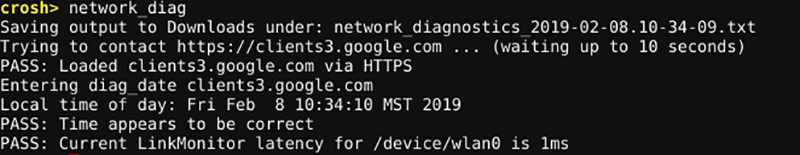
If you've run a ping test and tried configuring your modem, but you are still encountering issues, type this command to run a complete diagnosis on your network:
network_diagThe output will be saved as a TXT file in your Chromebook's storage.
13. Trace the Packet Route
The final Crosh networking command on this list lets you trace the route of the received data packets across a network. Run this command to check the packet route for google.com:
tracepath google.com14. Get Command-Line Help
If you are looking for a command not covered in this list, you can get a short or a full list of all the Crosh commands that are available to you.
To get a brief list of commands:
helpTo get a full list of commands, type:
help_advanced15. Memory Information
If you are looking to get information about your Chromebook's memory usage, you can go for one of the following two Crosh commands.
For an overview:
freeFor detailed information:
meminfo16. Switch to the Canary Channel
You can subscribe to different channels depending on what kind of updates you want on your Chromebook. There are four main channels available.
- Stable is for reliable and tested updates.
- With Beta, you get tested and fairly reliable latest features.
- Dev channel offers the latest updates that might not be very reliable.
- Then, there is the Canary channel, which offers experimental updates with bleeding-edge features but very little reliability.
The name of this experimental channel is derived from the proverb, "Canary in a coal mine." You can switch to this channel and live on the edge using the command below:
live_in_a_coal_mine17. Auto-Updates Over Cellular Networks
By default, Chrome OS doesn't update the system while you are on a cellular network. It's the same as on Android. If using mobile internet is not an issue for you, you can turn automatic updates over cellular networks on or off using these commands:
update_over_cellular enable
update_over_cellular disable18. Exit Crosh
When you've finished exploring and want to close the shell, just type:
exitIt's as simple as that.
Make Backups Before You Begin
It goes without saying that if you change settings in the Chrome OS Developer Shell without knowing what you're doing, you could render your system unusable.
Luckily, Chromebooks are remarkably easy to restore, but you would lose any locally-saved data. As such, make sure you create backups before you do too much poking around.
So, enjoy exploring your Chromebook by tinkering with the Crosh commands listed above.
![How to Find IMSI Number on iPhone [Helps with iOS Unlock][Updated] data:post.title](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjLjHwhnfUXNJTuiylqmlurhLRVAEVi803j6xcnvN8EZwF5_XUynz1y0Ko-vwpx6O3nT5hogTELahedGzgQpXM5Y99fcBliinyBu8ACw8_DVV3FpPLkIqR0u7v_HM39rAkpV5MyJiG1h5s/s72-c/find+imsi+iphone.jpg)